Artificial turf has revolutionized the world of sports, especially in football, where the demand for year-round playable surfaces has escalated. The transition from natural grass to synthetic alternatives offers a solution to the challenges of weather and heavy foot traffic.
However, when it comes to choosing the ideal surface for a football field, two distinct types of artificial turf dominate the conversation: infilled and non-filled. The decision between these options can significantly influence game performance, safety, and long-term sustainability. Understanding the differences between these turf types is crucial to ensuring a playing surface that meets the specific needs of players, teams, and clubs alike.
Understanding the Two Types of Artificial Turf
Infilled Artificial Turf: Key Features and Composition
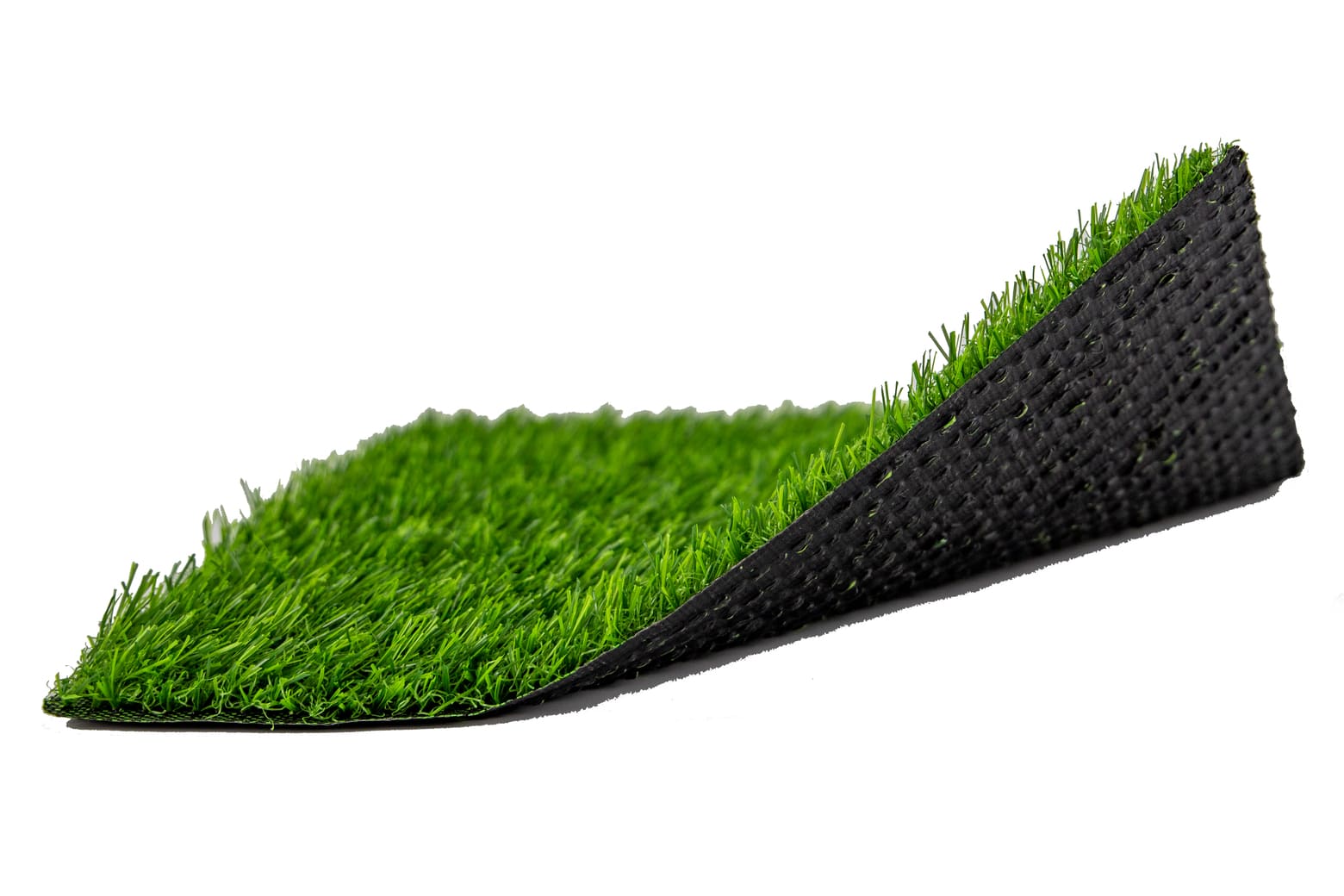
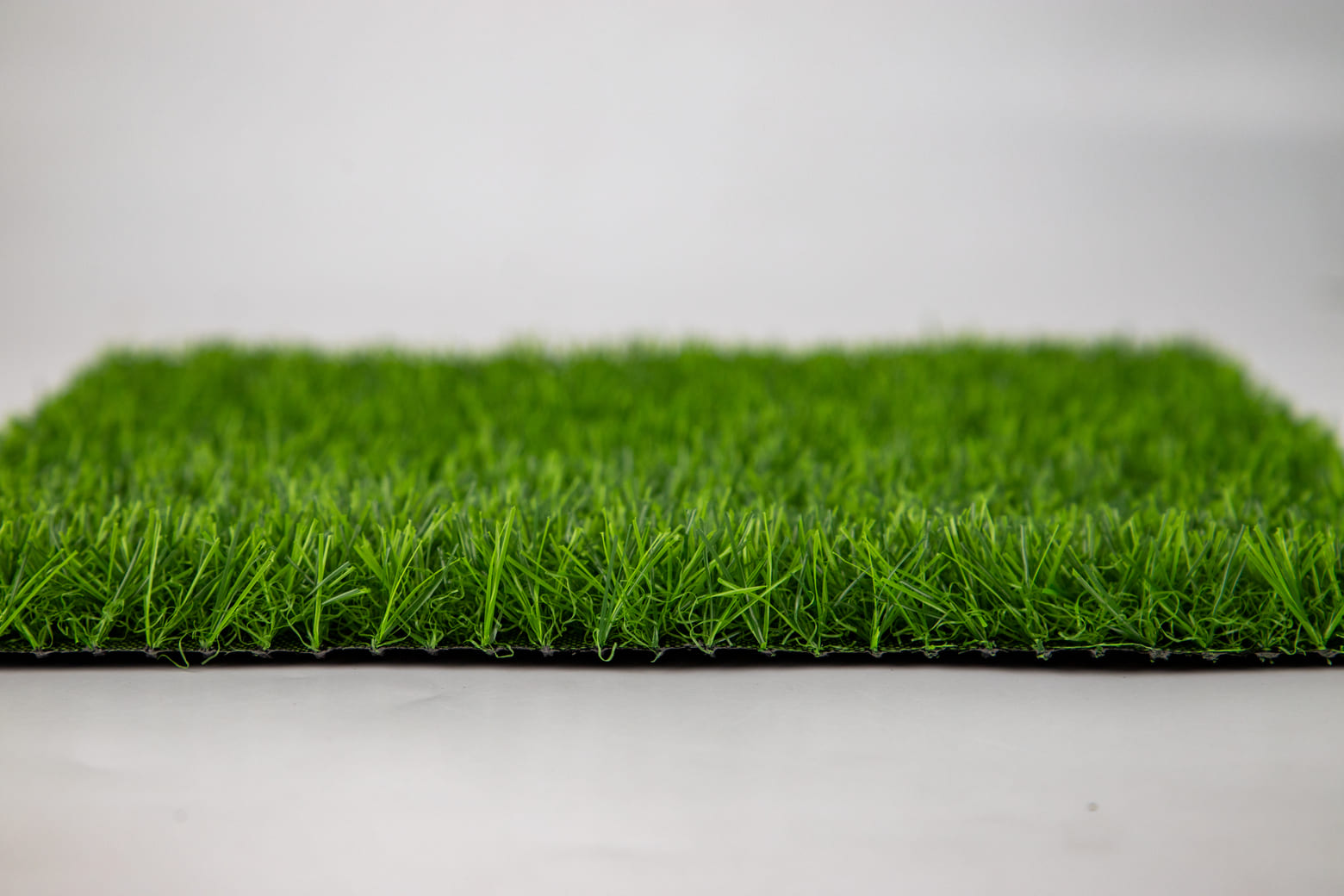
Infilled artificial turf is composed of synthetic fibers that are woven into a durable backing material. What sets this type of turf apart is the use of infill materials, typically sand and rubber granules, which are spread between the blades of grass. This infill serves several key purposes: it provides stability to the fibers, enhances shock absorption, and simulates the cushioning effects of natural grass. Infilled turf is highly favored for its ability to replicate the feel of real grass, offering a playing surface that is firm yet forgiving.
The blend of materials in infilled artificial turf can vary, with some fields opting for eco-friendly, biodegradable infill options to reduce environmental impact. These fields are particularly popular in high-performance settings, where both playability and safety are paramount.
Non-Filled Artificial Turf: Characteristics and Differences
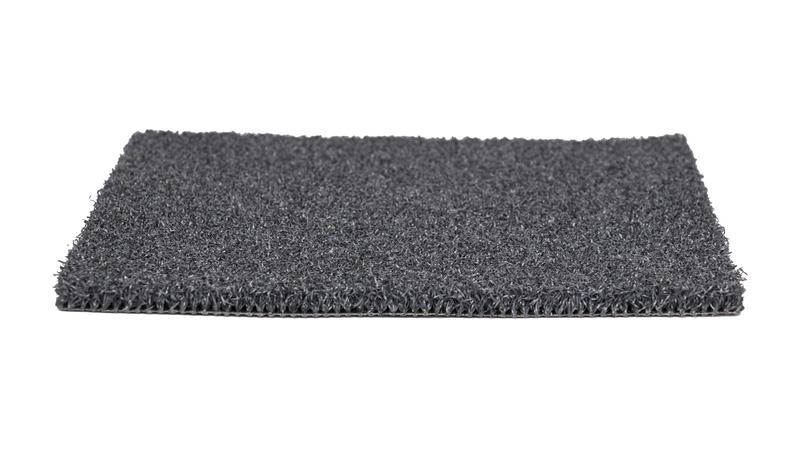
Non-filled artificial turf, on the other hand, omits the infill material altogether. The synthetic fibers are generally thicker and have been engineered to stand upright without the need for additional support. As such, non-filled turf is often perceived as more durable and less maintenance-intensive because there is no need to replace or top up the infill. This type of turf tends to have a slightly stiffer surface compared to its infilled counterpart, offering less shock absorption and potentially increasing the risk of player injuries, particularly during hard tackles or falls.
The absence of infill can result in a faster, firmer surface, which may be advantageous for certain types of play, such as fast-paced, passing-oriented football. Non-filled turf is also known for its ability to retain its shape over time, reducing the need for ongoing maintenance to keep the fibers upright.
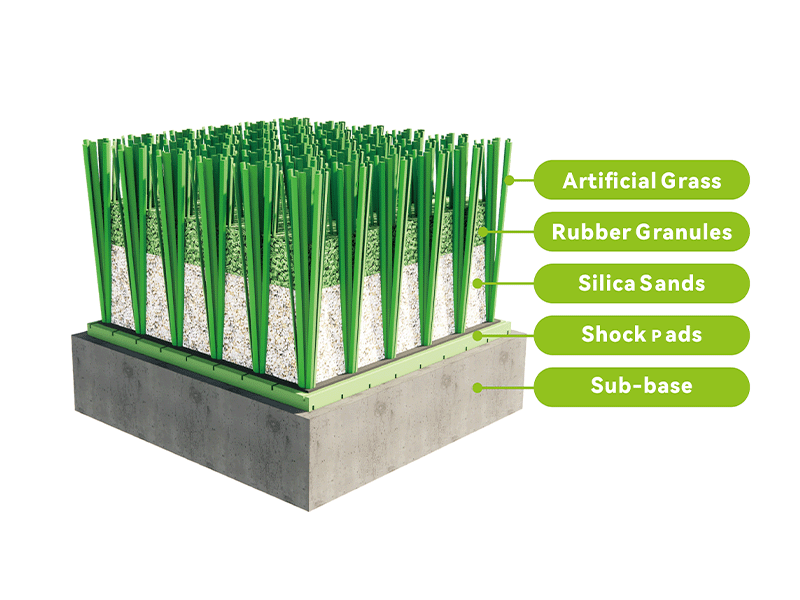
Infilled Football Artificial Turf Structure
Performance Factors
Playability and Ball Behavior
The performance of artificial turf directly affects the dynamics of the game, including ball control, bounce, and speed. Infilled turf tends to replicate the behavior of natural grass more closely. The presence of rubber and sand in the infill creates a softer, more responsive surface, which allows the ball to roll with a more natural trajectory. The shock absorption provided by the infill also results in less unpredictable ball bounce, giving players better control during passes and shots.
Conversely, non-filled turf tends to offer a faster surface, where the ball travels more quickly due to its firmer, denser nature. However, the lack of infill can cause the ball to bounce unpredictably, which can lead to irregularities in ball control. While some players may prefer the speed of non-filled turf, others may find the inconsistency in ball behavior challenging, especially in competitive settings.
Injury Prevention and Player Comfort
One of the most critical factors in selecting artificial turf is its impact on player safety. Infilled turf has the advantage of enhanced shock absorption, thanks to the cushioning effect of the infill materials. This results in a more forgiving surface, which can reduce the likelihood of injuries like sprains, strains, and concussions, especially during high-impact situations. The additional layer of protection makes it a preferred choice for youth leagues and professional teams alike.
Non-filled turf, while durable, offers less cushioning and can increase the risk of certain injuries, particularly on hard tackles or during rough falls. The increased stiffness of the surface places more stress on joints, leading to a higher incidence of injuries such as knee and ankle strains. As a result, non-filled turf might be better suited for training fields or situations where durability and low maintenance are prioritized over player comfort and safety.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Durability is a key consideration for any football field, especially in high-use environments. Infilled artificial turf generally requires more maintenance due to the need to replace or top-up the infill materials periodically. Over time, the infill can become compacted or displaced, leading to uneven playing surfaces. This requires regular maintenance to ensure the surface remains stable and functional.
Non-filled turf, in contrast, requires less frequent maintenance because the absence of infill eliminates the need for replenishing or adjusting materials. Its design is inherently more durable, with the synthetic fibers standing upright without the risk of becoming compacted. However, non-filled turf can still require periodic cleaning and brushing to maintain optimal performance.
FIFA Standard Infilled Football Grass
Environmental Considerations
Heat Retention and Surface Temperature
Artificial turf, regardless of type, tends to retain heat, especially in hot climates or during midday sun. Infilled turf, with its rubber components, can absorb and retain heat more effectively, creating a surface temperature that may exceed 150°F on hot days. This can affect both player comfort and the longevity of the turf. Non-filled turf, while still susceptible to heat retention, generally experiences lower surface temperatures due to the absence of rubber, making it a more comfortable choice during extreme heat.
Drainage Efficiency and Water Runoff
The drainage capabilities of artificial turf play a significant role in how well it performs during rainy conditions. Infilled turf typically features a perforated backing that allows water to drain through the infill material and into the base below. While this helps prevent puddles and water accumulation, improper installation can lead to drainage issues over time.
Non-filled turf, with its smoother surface and fewer layers, tends to offer better drainage, allowing water to flow more freely through the fibers. This can reduce the risk of waterlogged fields and ensure a consistently dry playing surface during adverse weather conditions.
Sustainability and Recycling
The environmental impact of artificial turf is a growing concern, with both infilled and non-filled options presenting challenges. Infilled turf, especially those using rubber granules made from recycled tires, can present issues at the end of the turf's lifecycle. While some manufacturers are working toward eco-friendly infill options, the rubber can still be difficult to recycle.
Non-filled turf is often considered more sustainable in this regard, as it typically involves fewer materials and less environmental impact. Additionally, some non-filled turf systems are designed to be fully recyclable, contributing to a more sustainable solution for sports fields.
Non-filled Football Artificial Turf
Cost Analysis
Initial Installation Costs
The upfront cost of artificial turf installation can vary depending on the type and size of the field. Infilled artificial turf tends to be more expensive due to the complexity of its design and the additional materials required for infill. Non-filled turf may come at a lower initial cost due to its simpler structure and fewer materials.
Long-Term Maintenance and Replacement Costs
Long-term costs are another critical factor to consider. Infilled turf, while offering a more natural playing experience, requires more frequent maintenance, including infill replenishment and adjustments to ensure uniformity. Over time, these ongoing costs can add up, making infilled turf a higher long-term investment.
Non-filled turf, while requiring less maintenance, can be more durable and cost-effective over time, as the absence of infill reduces maintenance efforts. However, its higher initial installation cost may be offset by its longer lifespan and lower upkeep.
Return on Investment for Football Clubs
When evaluating the return on investment, football clubs must balance initial installation costs with the expected lifespan and maintenance requirements of the turf. Infilled turf, with its superior playability and player safety benefits, may be worth the additional investment for high-level competition fields. Non-filled turf, however, offers a more cost-efficient solution for clubs looking for a durable, low-maintenance surface.
Conclusion
Infilled and non-filled artificial turf each offer distinct advantages, and the choice between the two depends on the specific needs and priorities of the football field in question. Infilled turf excels in providing a more natural playing experience with better shock absorption and player safety, making it the preferred choice for high-performance settings. On the other hand, non-filled turf offers a durable, low-maintenance alternative, making it an attractive option for clubs looking to minimize ongoing costs while still providing a playable surface.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by a thorough assessment of performance, maintenance, environmental impact, and budget. If you want further information about infilled and non-filled artificial turf, please feel free to contact Citygreen Turf, a FIFA-graded football artificial turf manufacturer in China, at sales@city-green.com.